Introduction
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a class of deep learning models introduced by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in 2014. The core idea behind GANs is to train a generator network to produce data that is indistinguishable from real data, while simultaneously training a discriminator network to differentiate between real and generated data.
- Architecture overview: GANs consist of two main components: the generator and the discriminator
- Generator: The generator takes random noise z as input and generates synthetic data samples. Its goal is to create data that is realistic enough to deceive the discriminator.
- Discriminator: The discriminator, akin to a detective, evaluates whether a given sample is real (from the actual dataset) or fake (generated by the generator). Its objective is to become increasingly accurate in distinguishing between real and generated samples.

Backpropogation
Now, we will go through some simple equations. The discriminator outputs a value D(x) indicating the chance that x is a real image. Our objective is to maximize the chance to recognize real images as real and generated images as fake. i.e. the maximum likelihood of the observed data. To measure the loss, we use cross-entropy as in most Deep Learning: p log(q). For real image, p (the true label for real images) equals to 1. For generated images, we reverse the label (i.e. one minus label). So the objective becomes:
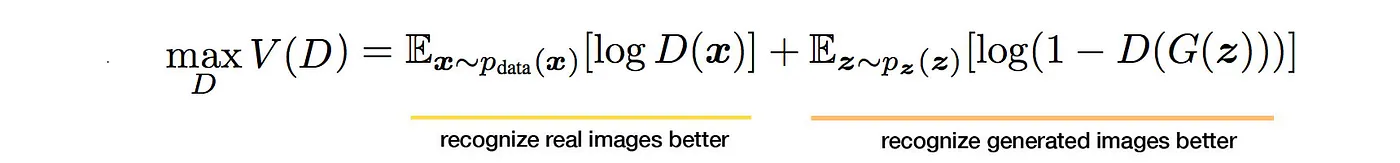 On the generator side, its objective function wants the model to generate images with the highest possible value of D(x) to fool the discriminator.
On the generator side, its objective function wants the model to generate images with the highest possible value of D(x) to fool the discriminator.
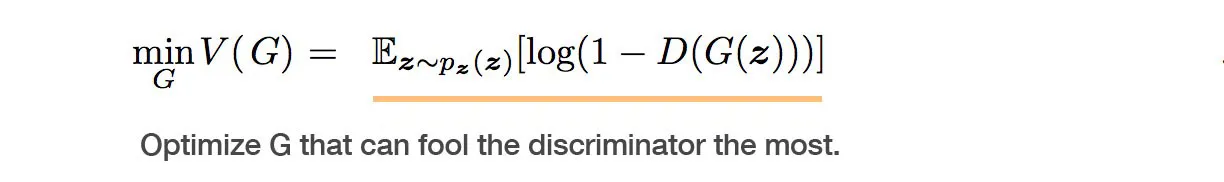
Code
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import math
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
os.makedirs("images", exist_ok=True)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=200, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0002, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=8, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--latent_dim", type=int, default=100, help="dimensionality of the latent space")
parser.add_argument("--img_size", type=int, default=28, help="size of each image dimension")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=1, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=400, help="interval betwen image samples")
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
img_shape = (opt.channels, opt.img_size, opt.img_size)
cuda = True if torch.cuda.is_available() else False
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
def block(in_feat, out_feat, normalize=True):
layers = [nn.Linear(in_feat, out_feat)]
if normalize:
layers.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_feat, 0.8))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
return layers
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*block(opt.latent_dim, 128, normalize=False),
*block(128, 256),
*block(256, 512),
*block(512, 1024),
nn.Linear(1024, int(np.prod(img_shape))),
nn.Tanh()
)
def forward(self, z):
img = self.model(z)
img = img.view(img.size(0), *img_shape)
return img
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(int(np.prod(img_shape)), 512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(256, 1),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
def forward(self, img):
img_flat = img.view(img.size(0), -1)
validity = self.model(img_flat)
return validity
# Loss function
adversarial_loss = torch.nn.BCELoss()
# Initialize generator and discriminator
generator = Generator()
discriminator = Discriminator()
if cuda:
generator.cuda()
discriminator.cuda()
adversarial_loss.cuda()
# Configure data loader
os.makedirs("../../data/mnist", exist_ok=True)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(
"../../data/mnist",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(opt.img_size), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])]
),
),
batch_size=opt.batch_size,
shuffle=True,
)
# Optimizers
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if cuda else torch.FloatTensor
# ----------
# Training
# ----------
for epoch in range(opt.n_epochs):
for i, (imgs, _) in enumerate(dataloader):
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = Variable(Tensor(imgs.size(0), 1).fill_(1.0), requires_grad=False)
fake = Variable(Tensor(imgs.size(0), 1).fill_(0.0), requires_grad=False)
# Configure input
real_imgs = Variable(imgs.type(Tensor))
# -----------------
# Train Generator
# -----------------
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Sample noise as generator input
z = Variable(Tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (imgs.shape[0], opt.latent_dim))))
# Generate a batch of images
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# Loss measures generator's ability to fool the discriminator
g_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs), valid)
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# Measure discriminator's ability to classify real from generated samples
real_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(real_imgs), valid)
fake_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs.detach()), fake)
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
print(
"[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f]"
% (epoch, opt.n_epochs, i, len(dataloader), d_loss.item(), g_loss.item())
)
batches_done = epoch * len(dataloader) + i
if batches_done % opt.sample_interval == 0:
save_image(gen_imgs.data[:25], "images/%d.png" % batches_done, nrow=5, normalize=True)